implementation("io.micronaut.mcp:micronaut-mcp-server-java-sdk")Disk Space MCP Server with STDIO transport
Build a MCP Server with STDIO transport to expose your machine diskspace.
Authors: Sergio del Amo
Micronaut Version: 4.10.9
1. Getting Started
In this guide, we will create a Micronaut application written in Java.
2. What you will need
To complete this guide, you will need the following:
-
Some time on your hands
-
A decent text editor or IDE (e.g. IntelliJ IDEA)
-
JDK 21 or greater installed with
JAVA_HOMEconfigured appropriately
3. Solution
We recommend that you follow the instructions in the next sections and create the application step by step. However, you can go right to the completed example.
-
Download and unzip the source
Create an application using the Micronaut Command Line Interface or with Micronaut Launch.
4. Dependency
Add the Micronaut MCP Server Java SDK dependency to your build file:
5. Configuration
micronaut.mcp.server.info.name=Disk Space
micronaut.mcp.server.info.version=0.0.1
(1)
micronaut.mcp.server.transport=STDIO| 1 | To use STDIO transport. |
6. Disk Utils
Create a utility class to get the disk space information of the computer.
package example.micronaut;
import java.io.File;
public final class DiskUtils {
private DiskUtils() {}
public static String freeDiskSpace() {
File root = new File("/");
long freeBytes = root.getFreeSpace();
double freeGB = freeBytes / (1024.0 * 1024 * 1024);
return String.format("Free disk space: %.2f GB", freeGB);
}
}7. MCP Tool
Next, we are going to create an MCP Tool that exposes the disk space information.
Tools: Executable functions that allow models to perform actions or retrieve information
package example.micronaut;
import io.micronaut.mcp.annotations.Tool;
import jakarta.inject.Singleton;
import java.io.File;
@Singleton (1)
class MyTools {
@Tool(title = "Free Disk Space",
description = "Return the free disk space in the users computer") (2)
String freeDiskSpace() {
return DiskUtils.freeDiskSpace();
}
}| 1 | Use jakarta.inject.Singleton to designate a class as a singleton. |
| 2 | Annotate a method with @Tool to expose it as an MCP Tool. |
8. STDOUT
When using the STDIO transport, it is important to ensure that the application does not write any logs or other output to stdout, as this would interfere with the MCP protocol communication.
Disable the Micronaut banner
package example.micronaut;
import io.micronaut.runtime.Micronaut;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Micronaut.build(args)
.banner(false)
.start();
}
}Configure Logback not to log to stdout. For example, you can configure Logback to log to a file or to stderr (see <target>System.err</target> in the configuration file below):
<configuration>
<appender name="STDERR" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<target>System.err</target>
<!-- encoders are assigned the type
ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder by default -->
<encoder>
<pattern>%cyan(%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS}) %gray([%thread]) %highlight(%-5level) %magenta(%logger{36}) - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="STDERR" />
</root>
</configuration>9. Executable JAR
Create an executable jar including all dependencies:
./gradlew shadowJar10. MCP Inspector
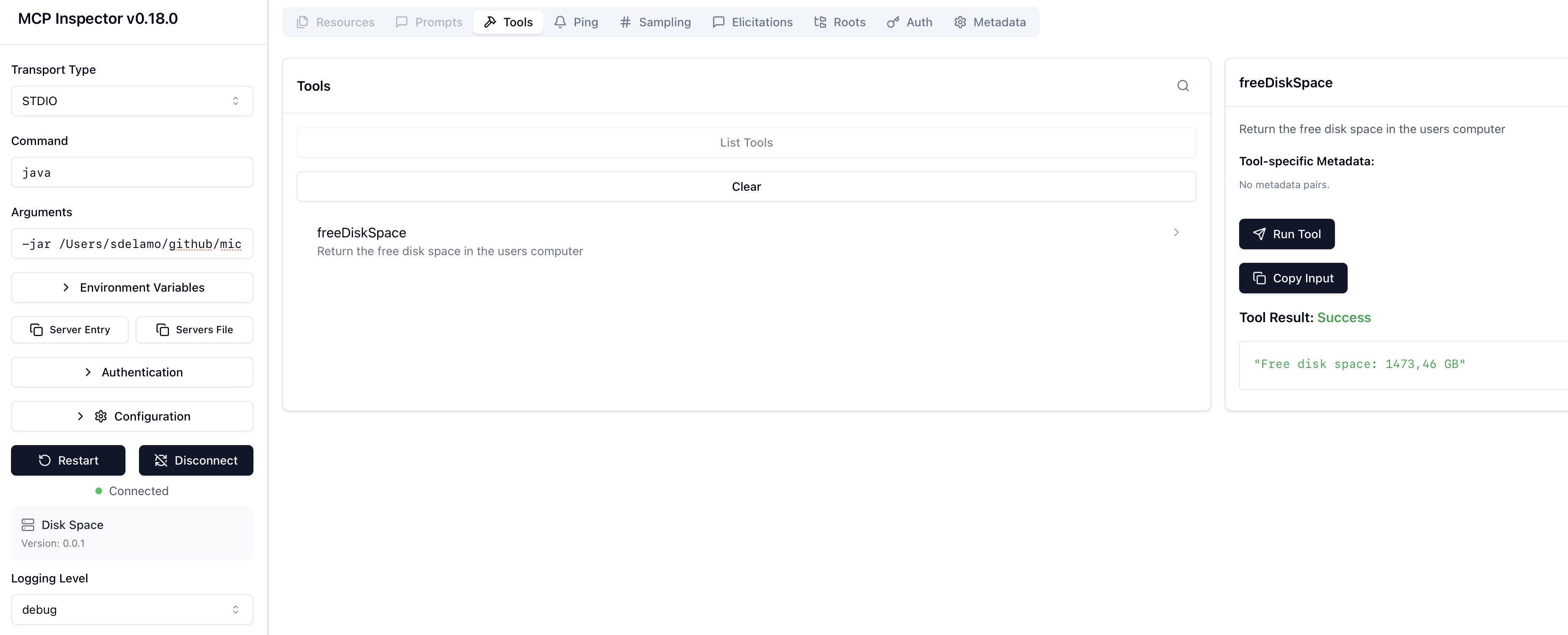
To test the MCP Server, run the MCP inspector.
Select STDIO as Transport type.
Enter java as Command.
Enter -jar PATH_TO_YOUR_PROJECT/build/libs/default-0.1-all.jar as Arguments.
Click connect. You will be able to list tools and invoke the freeDiskSpace tool.
11. Next Steps
Explore more features with Micronaut Guides.
Check the Micronaut MCP documentation and the Micronaut MCP Guides
12. License
| All guides are released with an Apache license 2.0 license for the code and a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license for the writing and media (images…). |