<dependency>
<groupId>io.micronaut.mcp</groupId>
<artifactId>micronaut-mcp-server-java-sdk</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>MCP Weather Server with STDIO transport
Build a MCP weather Server with STDIO transport.
Authors: Sergio del Amo
Micronaut Version: 4.10.9
1. Getting Started
In this guide, we will create a Micronaut application written in Java.
2. What you will need
To complete this guide, you will need the following:
-
Some time on your hands
-
A decent text editor or IDE (e.g. IntelliJ IDEA)
-
JDK 21 or greater installed with
JAVA_HOMEconfigured appropriately
3. Solution
We recommend that you follow the instructions in the next sections and create the application step by step. However, you can go right to the completed example.
-
Download and unzip the source
Create an application using the Micronaut Command Line Interface or with Micronaut Launch.
4. What will you build?
In this guide, we will create an MCP Server with Micronaut as the one described in the Build an MCP server tutorial on the Model Context Protocol website.
5. Dependency
Add the Micronaut MCP Server Java SDK dependency to your build file:
To use Micronaut JSON Schema generation capabilities, add the following dependencies:
<!-- Add the following to your annotationProcessorPaths element -->
<path>
<groupId>io.micronaut.jsonschema</groupId>
<artifactId>micronaut-json-schema-processor</artifactId>
</path>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micronaut.jsonschema</groupId>
<artifactId>micronaut-json-schema-annotations</artifactId>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>6. Configuration
micronaut.mcp.server.info.name=Weather
micronaut.mcp.server.info.version=0.0.1
(1)
micronaut.mcp.server.transport=STDIO| 1 | To use STDIO transport. |
7. JSON Schema Generation
An MCP Tool can define its input schema using JSON Schema.
Thanks to Micronaut JSON Schema, we can generate the JSON Schema at compile-time given a Java file.
Create two Java records to model the tools' inputs.
GetAlertInput will be the input schema of the getAlerts tool.
package example.micronaut;
import io.micronaut.jsonschema.JsonSchema;
import io.micronaut.serde.annotation.Serdeable;
/**
*
* @param state Two-letter US state code (e.g. CA, NY)
*/
@Serdeable (1)
@JsonSchema (2)
public record GetAlertInput(String state) {
}| 1 | Declare the @Serdeable annotation at the type level in your source code to allow the type to be serialized or deserialized. |
| 2 | Annotate the class with @JsonSchema to generate a JSON Schema for class during build time. |
Point will be the input schema of the getWeatherForecastByLocation tool.
package example.micronaut;
import io.micronaut.jsonschema.JsonSchema;
import io.micronaut.serde.annotation.Serdeable;
/**
*
* @param latitude Latitude of the location
* @param longitude Longitude of the location
*/
@Serdeable
@JsonSchema
public record Point(double latitude, double longitude) {
}| 1 | Declare the @Serdeable annotation at the type level in your source code to allow the type to be serialized or deserialized. |
| 2 | Annotate the class with @JsonSchema to generate a JSON Schema for class during build time. |
8. MCP Tool
The MCP Server exposes two tools: getWeatherForecastByLocation and getAlerts.
package example.micronaut;
import example.micronaut.weather.WeatherClient;
import io.micronaut.mcp.annotations.Tool;
import jakarta.inject.Singleton;
@Singleton (1)
class Tools {
private final WeatherClient weatherClient;
Tools(WeatherClient weatherClient) { (2)
this.weatherClient = weatherClient;
}
@Tool(description = "Get weather forecast for a specific latitude/longitude coordinates") // 3>
String getWeatherForecastByLocation(Point point) {
return weatherClient.formattedForecast(point.latitude(), point.longitude());
}
@Tool(description = "Get weather alerts for a US state") // 3>
String getAlerts(GetAlertInput input) {
return weatherClient.formattedAlerts(input.state());
}
}| 1 | Use jakarta.inject.Singleton to designate a class as a singleton. |
| 2 | Use constructor injection to inject a bean of type WeatherClient. |
| 3 | Annotate a method with @Tool to expose it as an MCP Tool. |
WeatherClient is a Micronaut bean which uses the Micronaut HTTP Client to consume
https://api.weather.gov API. Please, download the complete project to check the code.
9. STDOUT
When using the STDIO transport, it is important to ensure that the application does not write any logs or other output to stdout, as this would interfere with the MCP protocol communication.
Disable the Micronaut banner
package example.micronaut;
import io.micronaut.runtime.Micronaut;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Micronaut.build(args)
.banner(false)
.start();
}
}Configure Logback not to log to stdout. For example, you can configure Logback to log to a file or to stderr (see <target>System.err</target> in the configuration file below):
<configuration>
<appender name="STDERR" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<target>System.err</target>
<!-- encoders are assigned the type
ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder by default -->
<encoder>
<pattern>%cyan(%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS}) %gray([%thread]) %highlight(%-5level) %magenta(%logger{36}) - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="STDERR" />
</root>
</configuration>10. Executable JAR
Create an executable jar including all dependencies:
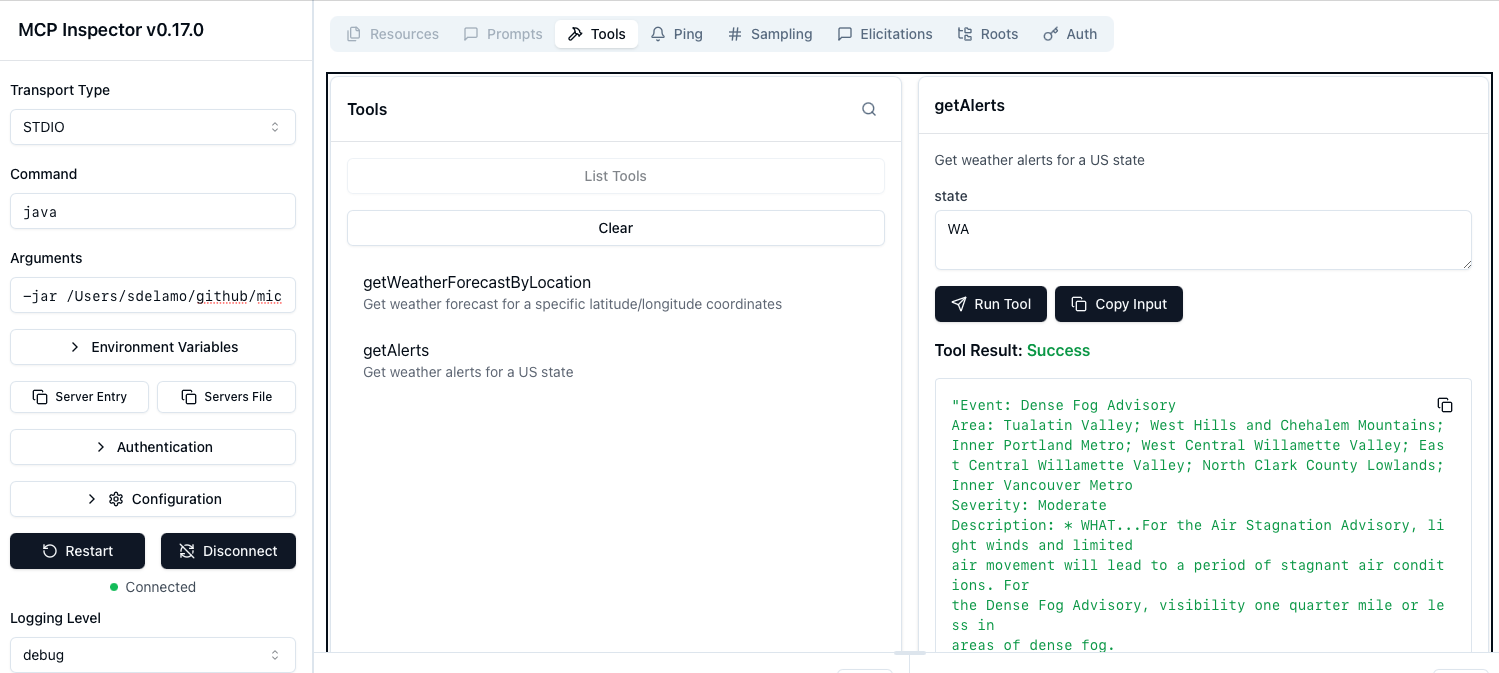
./mvnw package11. MCP Inspector
To test the MCP Server, run the MCP inspector.
Select STDIO as Transport type.
Enter java as Command.
Enter -jar PATH_TO_YOUR_PROJECT/target/default-0.1.jar as Arguments.
Click connect.
You will be able to list tools and invoke the getWeatherForecastByLocation tool.
| The https://api.weather.gov API works only for US locations. |
and the getAlerts tool.
12. Next Steps
Explore more features with Micronaut Guides.
Check the Micronaut MCP documentation and the Micronaut MCP Guides
13. License
| All guides are released with an Apache license 2.0 license for the code and a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license for the writing and media (images…). |