mn create-function-app example.micronaut.micronautguide \
--features=aws-lambda \
--build=gradle \
--lang=javaMicronaut RequestStreamHandler to Lambda Java Runtime.
Learn how to deploy a Micronaut function to AWS Lambda Java Runtime with an AWS Lambda RequestStreamHandler.
Authors: Sergio del Amo
Micronaut Version: 4.10.9
In this guide, we will deploy a Micronaut serverless function to AWS Lambda using a RequestStreamHandler.
1. Getting Started
In this guide, we will create a Micronaut application written in Java.
2. What you will need
To complete this guide, you will need the following:
-
Some time on your hands
-
A decent text editor or IDE (e.g. IntelliJ IDEA)
-
JDK 21 or greater installed with
JAVA_HOMEconfigured appropriately
3. Solution
We recommend that you follow the instructions in the next sections and create the application step by step. However, you can go right to the completed example.
-
Download and unzip the source
4. Writing the Application
Create an application using the Micronaut Command Line Interface or with Micronaut Launch.
If you don’t specify the --build argument, Gradle with the Kotlin DSL is used as the build tool. If you don’t specify the --lang argument, Java is used as the language.If you don’t specify the --test argument, JUnit is used for Java and Kotlin, and Spock is used for Groovy.
|
If you use Micronaut Launch, select serverless function as application type and add the aws-lambda feature.
The previous command creates a Micronaut application with the default package example.micronaut in a directory named micronautguide.
4.1. RequestStreamHandler
To use your own serialization, implement the RequestStreamHandler interface. With this interface, Lambda passes your handler an input stream and output stream. The handler reads bytes from the input stream, writes to the output stream, and returns void.
The application contains a class extending MicronautRequestStreamHandler
Replace the generated FunctionRequestHandler.java with the following:
package example.micronaut;
import io.micronaut.context.env.Environment;
import io.micronaut.core.annotation.Introspected;
import io.micronaut.function.aws.MicronautRequestStreamHandler;
@Introspected
public class FunctionRequestHandler extends MicronautRequestStreamHandler { (1)
@Override
protected String resolveFunctionName(Environment env) {
return "requestfunction"; (2)
}
}| 1 | The class extends MicronautRequestStreamHandler |
| 2 | It specifies a function name. |
You will use MicronautRequestStreamHandler in combination of a class annotated with @FunctionBean which implements one of the interfaces from the java.util.function package.
package example.micronaut;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.events.APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.events.APIGatewayProxyResponseEvent;
import io.micronaut.function.FunctionBean;
import io.micronaut.json.JsonMapper;
import jakarta.inject.Inject;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.function.Function;
@FunctionBean("requestfunction") (1)
public class RequestFunction implements Function<APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent, APIGatewayProxyResponseEvent> { (2)
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RequestFunction.class);
@Inject (3)
JsonMapper jsonMapper;
@Override
public APIGatewayProxyResponseEvent apply(APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent requestEvent) {
LOG.info("request {}", requestEvent);
APIGatewayProxyResponseEvent response = new APIGatewayProxyResponseEvent();
try {
String json = new String(jsonMapper.writeValueAsBytes(Collections.singletonMap("message", "Hello World")));
response.setStatusCode(200);
response.setBody(json);
} catch (IOException e) {
response.setStatusCode(500);
}
LOG.info("response {}", response);
return response;
}
}| 1 | The class is annotated with @FunctionBean. It specifies requestfunction as an annotation value, which matches what we set in FunctionRequestHandler.. |
| 2 | It implements java.util.function.Function, which accepts a single argument and returns a single result. We use APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent and APIGatewayProxyResponseEvent from the AWS Lambda Java Events library. |
| 3 | Field injection |
4.2. Tests
You can test the handler behaves as expected, as shown in the following example:
package example.micronaut;
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.events.APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent;
import io.micronaut.json.JsonMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
class FunctionRequestHandlerTest {
private static FunctionRequestHandler handler;
@BeforeAll
public static void setupServer() {
handler = new FunctionRequestHandler(); (1)
}
@AfterAll
public static void stopServer() {
if (handler != null) {
handler.getApplicationContext().close(); (2)
}
}
@Test
void testHandler() throws IOException {
JsonMapper jsonMapper = handler.getApplicationContext().getBean(JsonMapper.class);
try (ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
InputStream inputStream = createInputStreamRequest(jsonMapper)) {
handler.execute(inputStream, baos); (3)
assertEquals("""
{"statusCode":200,"body":"{\\"message\\":\\"Hello World\\"}"}""", baos.toString());
}
}
private InputStream createInputStreamRequest(JsonMapper jsonMapper) throws IOException {
return new ByteArrayInputStream(jsonMapper.writeValueAsBytes(createRequest()));
}
private APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent createRequest() {
APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent request = new APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent();
request.setHttpMethod("GET");
request.setPath("/");
return request;
}
}| 1 | When you instantiate the Handler, the application context starts. |
| 2 | Remember to close your application context when you end your test. You can use your handler to obtain it. |
| 3 | Invoke the execute method of the handler. |
5. Testing the Application
To run the tests:
./gradlew testThen open build/reports/tests/test/index.html in a browser to see the results.
6. Lambda
Create a Lambda Function. As a runtime, select Java 21 or Java 17.
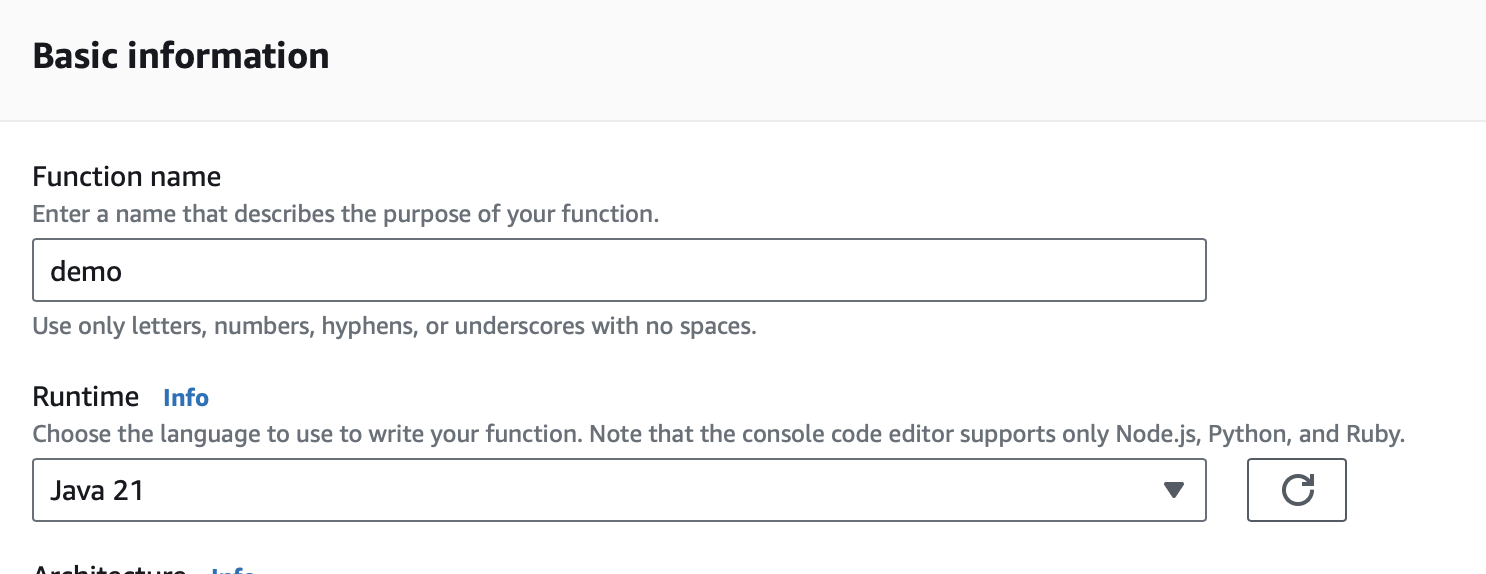
6.1. Upload Code
Create an executable jar including all dependencies:
./gradlew shadowJarUpload it:
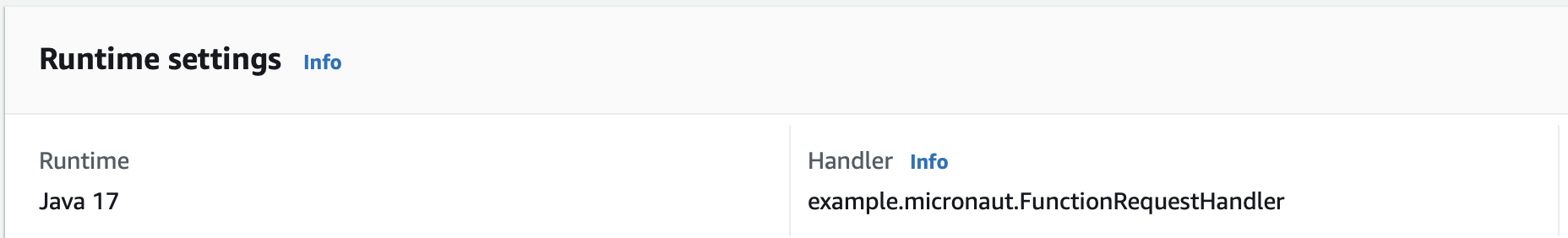
6.2. Handler
As Handler, set:
example.micronaut.FunctionRequestHandler
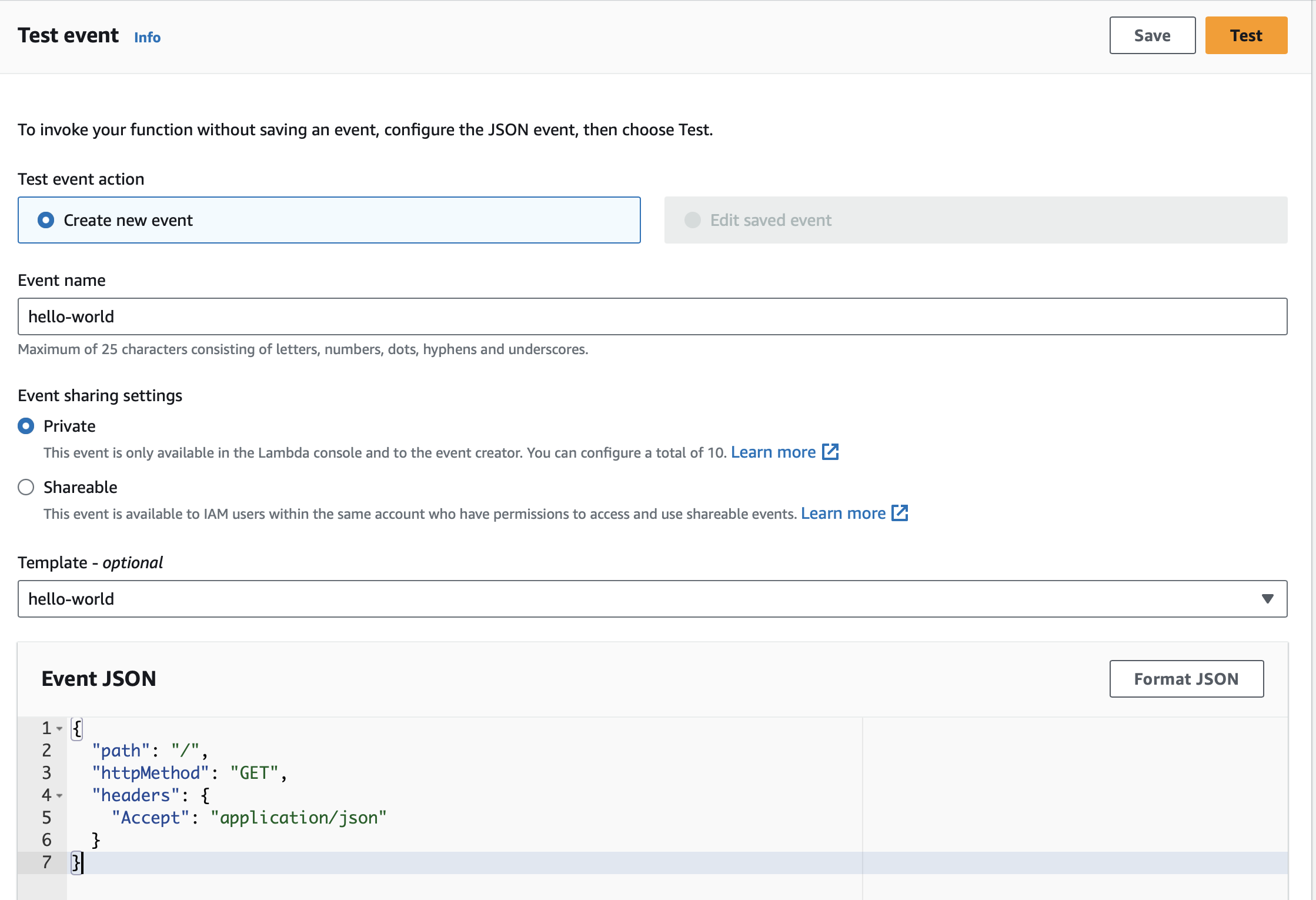
6.3. Test
You can test it easily with a JSON Event:
{
"path": "/",
"httpMethod": "GET",
"headers": {
"Accept": "application/json"
}
}When working with Amazon API Gateway, it’s easy to use apigateway-aws-proxy as an Event Template to get started:
You should see a 200 response:
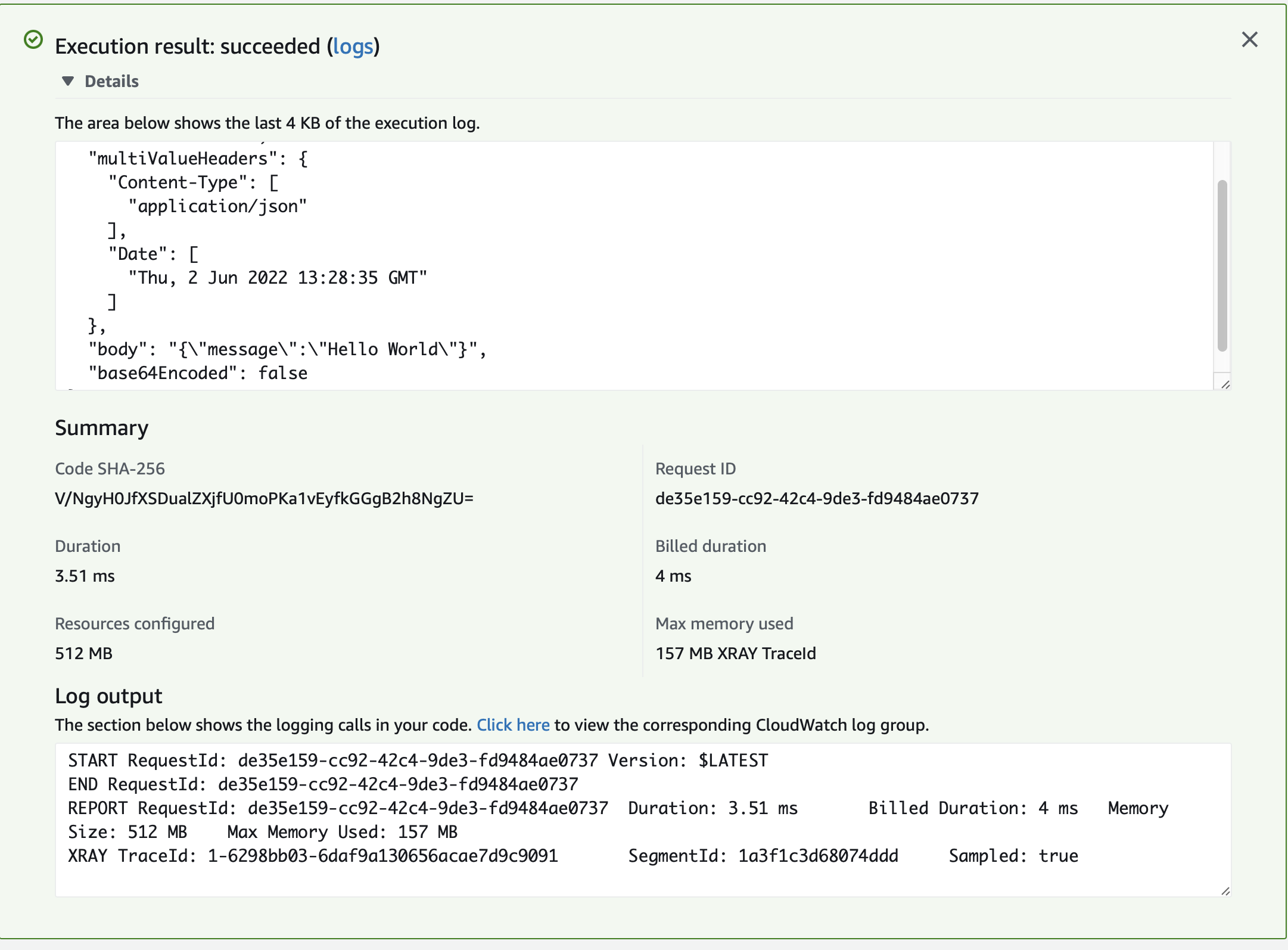
7. Next Steps
Explore more features with Micronaut Guides.
Read more about:
8. Help with the Micronaut Framework
The Micronaut Foundation sponsored the creation of this Guide. A variety of consulting and support services are available.
9. License
| All guides are released with an Apache license 2.0 license for the code and a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license for the writing and media (images…). |