mn create-function-app example.micronaut.micronautguide --features=aws-lambda --build=maven --lang=kotlinAWS Lambda Function URL and a Micronaut function
Deploy a Micronaut function to AWS Lambda Java 17 runtime and invoke it with a Lambda function URL.
Authors: Sergio del Amo
Micronaut Version: 4.10.9
In this guide, we will deploy a Micronaut serverless function to AWS Lambda Java 17 runtime and invoke it with a Lambda function URL.
1. Getting Started
In this guide, we will create a Micronaut application written in Kotlin.
2. What you will need
To complete this guide, you will need the following:
-
Some time on your hands
-
A decent text editor or IDE (e.g. IntelliJ IDEA)
-
JDK 21 or greater installed with
JAVA_HOMEconfigured appropriately
3. Solution
We recommend that you follow the instructions in the next sections and create the application step by step. However, you can go right to the completed example.
-
Download and unzip the source
4. Writing the Application
Create an application using the Micronaut Command Line Interface or with Micronaut Launch.
If you don’t specify the --build argument, Gradle with the Kotlin DSL is used as the build tool. If you don’t specify the --lang argument, Java is used as the language.If you don’t specify the --test argument, JUnit is used for Java and Kotlin, and Spock is used for Groovy.
|
If you use Micronaut Launch, select serverless function as application type and add the aws-lambda and aws-lambda-function-url features.
The previous command creates a Micronaut application with the default package example.micronaut in a directory named micronautguide.
5. Handler
Create a class extending MicronautRequestHandler and define input and output types.
package example.micronaut
import io.micronaut.function.aws.MicronautRequestHandler
import java.io.IOException
import io.micronaut.json.JsonMapper
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.events.APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.events.APIGatewayProxyResponseEvent
import jakarta.inject.Inject
class FunctionRequestHandler : MicronautRequestHandler<APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent, APIGatewayProxyResponseEvent>() {
@Inject
lateinit var objectMapper: JsonMapper
override fun execute(input: APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent): APIGatewayProxyResponseEvent =
APIGatewayProxyResponseEvent().apply {
try {
val json = String(objectMapper.writeValueAsBytes(mapOf("message" to "Hello World")))
statusCode = 200
body = json
} catch (e: IOException) {
statusCode = 500
}
}
}6. Handler Test
Write a test which verifies the function behaviour:
package example.micronaut
import com.amazonaws.services.lambda.runtime.events.APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
class FunctionRequestHandlerTest {
@Test
fun testHandler() {
val handler = FunctionRequestHandler()
val request = APIGatewayProxyRequestEvent()
request.httpMethod = "GET"
request.path = "/"
val response = handler.execute(request)
assertEquals(200, response.statusCode.toInt())
assertEquals("{\"message\":\"Hello World\"}", response.body)
handler.close()
}
}-
When you instantiate the Handler, the application context starts.
-
Remember to close your application context when you end your test. You can use your handler to obtain it.
-
Invoke the
executemethod of the handler.
7. Testing the Application
To run the tests:
./mvnw test8. Lambda
Create a Lambda Function. As a runtime, select Java 17, Java 21, or Java 25.
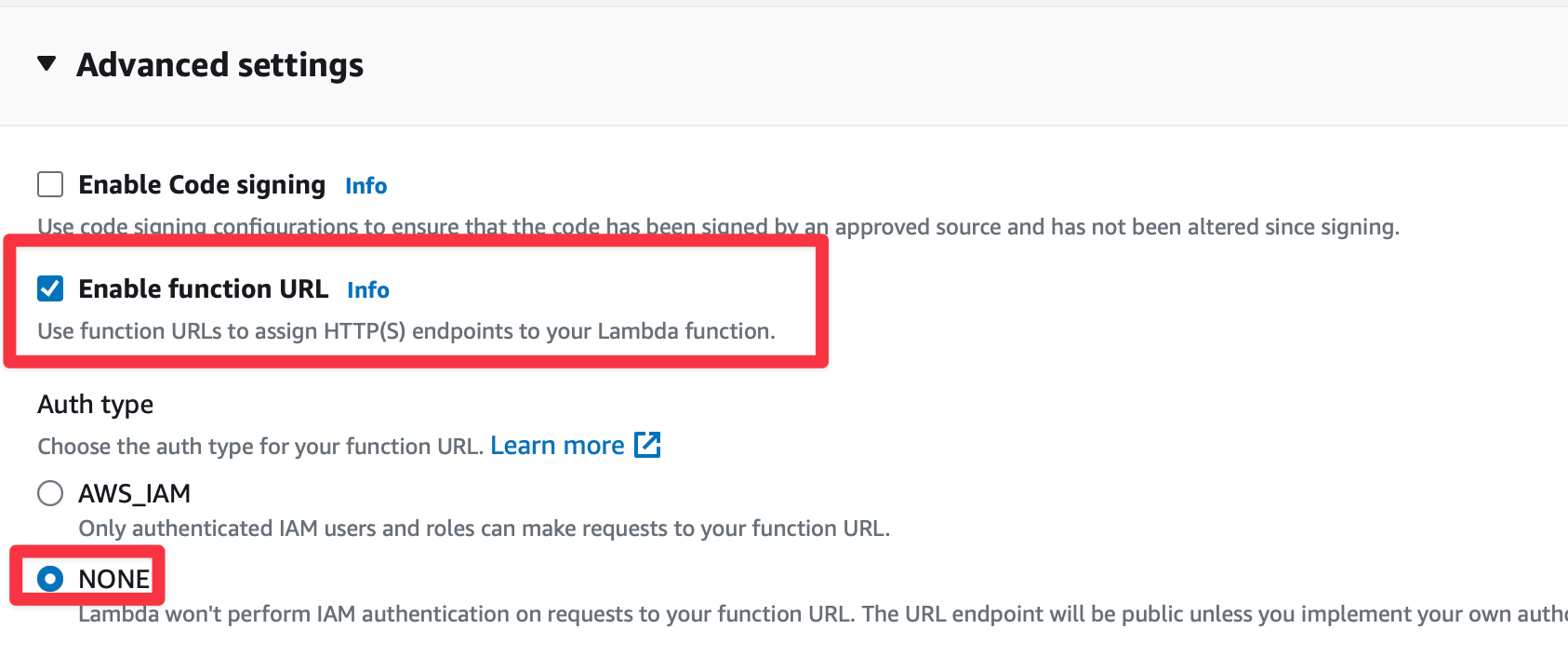
Enable function URLs and set Auth Type as NONE.
8.1. Upload Code
Create an executable jar including all dependencies:
./mvnw packageUpload it:
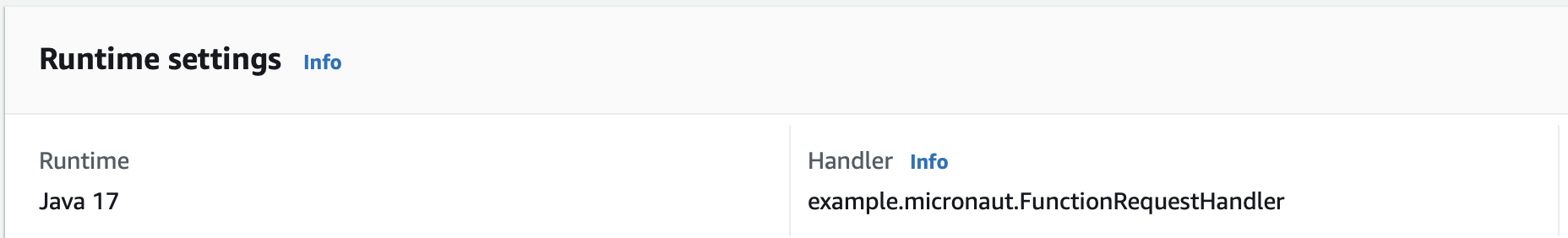
8.2. Handler
As Handler, set:
example.micronaut.FunctionRequestHandler
8.3. Obtain the Function URL
You can obtain the Function URL in the AWS Console:
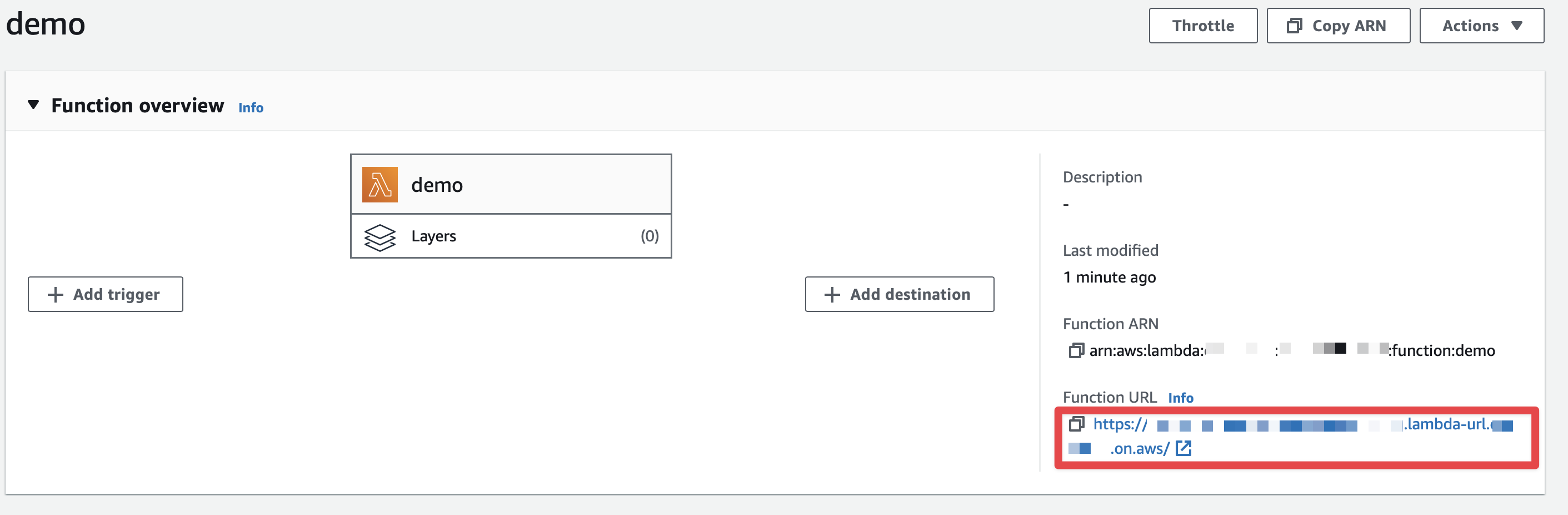
Invoke it, via a cURL command:
% curl -i https://xxxxxxxx.lambda-url.xxxx.on.aws/
{"message":"Hello World"}9. Next Steps
Explore more features with Micronaut Guides.
Read more about:
10. Help with the Micronaut Framework
The Micronaut Foundation sponsored the creation of this Guide. A variety of consulting and support services are available.
11. License
| All guides are released with an Apache license 2.0 license for the code and a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license for the writing and media (images…). |